Experiencing frustrating connectivity issues with your devices? A slow or unreliable network can significantly disrupt your work, entertainment, and daily online activities. Whether you’re dealing with Wi-Fi problems, internet outages, or trouble connecting to specific devices, resetting your network settings can often resolve these issues. This comprehensive troubleshooting guide will walk you through the process of resetting your network settings on various devices, helping you restore your connection and get back online quickly.
This guide covers resetting network settings for a variety of operating systems and devices, including Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and routers. We’ll explain the differences between various types of network resets, such as resetting Wi-Fi settings, cellular settings, and performing a full network reset. By understanding the implications of each reset, you can choose the most appropriate option to address your specific connectivity problem. This guide provides clear, step-by-step instructions, making the process accessible to users of all technical levels, helping you regain control of your network connection.
Understanding Network Settings and Their Importance
Network settings are the configuration parameters that control how your devices connect to and communicate with a network, whether it’s a local home network or the wider internet. These settings play a crucial role in establishing and maintaining a stable and secure connection.
They encompass various aspects of network communication, including:
- IP Address: A unique identifier for your device on the network.
- Subnet Mask: Defines the size of your local network.
- Default Gateway: The router that directs traffic to and from the internet.
- DNS Server: Translates domain names (e.g., google.com) into IP addresses.
- Wi-Fi Settings: Including network name (SSID), security protocol (e.g., WPA2), and password.
Incorrect or corrupted network settings can lead to a range of connectivity issues, preventing your devices from accessing the internet or other network resources. Understanding these settings is essential for troubleshooting and resolving these problems effectively.
Common Network Problems That Can Be Resolved by Resetting
Network problems can manifest in various frustrating ways. Resetting your network settings can often resolve these issues by clearing out incorrect configurations or corrupted data. Here are some common scenarios where a reset can be beneficial:
Inability to Connect to Wi-Fi: If your device can’t detect or connect to a Wi-Fi network, even networks it has successfully connected to before, a network reset might be the solution.
Slow Internet Speeds: Experiencing significantly slower internet speeds than expected? A reset can sometimes clear up bottlenecks and improve performance.
Intermittent Connection Drops: If your internet connection frequently drops or becomes unstable, resetting can help establish a more consistent connection.
Unable to Assign IP Address: Sometimes a device fails to obtain a valid IP address from the network. A reset can force the device to request a new IP address and rectify this issue.
DNS Server Issues: Problems with Domain Name System (DNS) servers can prevent websites from loading. A reset can often resolve these DNS-related problems.
How to Reset Network Settings on Different Devices
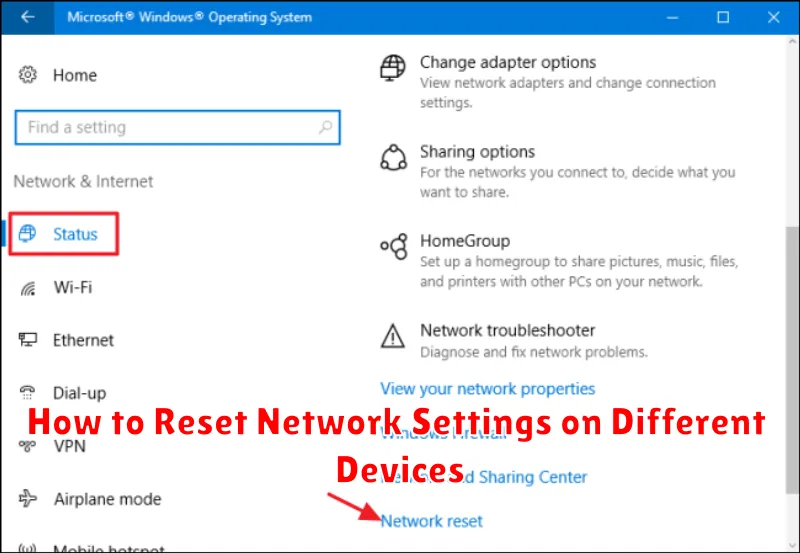
Resetting network settings can vary slightly depending on the operating system and device. Here’s a general guide for common platforms:
Windows
In Windows, navigate to Settings > Network & Internet > Status. Click Network reset. This will remove and reinstall all your network adapters and restore all network components to their original settings. You will need to reconnect to Wi-Fi networks afterward.
macOS
For macOS, go to System Preferences > Network. Select the network interface you want to reset (e.g., Wi-Fi, Ethernet), then click the Advanced button. Navigate to the TCP/IP tab and click Renew DHCP Lease. For a more thorough reset, delete the network interface and recreate it.
Android
On Android devices, the steps can vary by manufacturer, but generally, navigate to Settings > System > Reset options. You should find an option to Reset Wi-Fi, mobile & Bluetooth. This will reset all network connections.
iOS
For iOS (iPhone, iPad), go to Settings > General > Reset. Select Reset Network Settings. This will clear all network settings including Wi-Fi passwords and VPN configurations.
Restoring Network Connectivity After a Reset
After resetting your network settings, your device will be in a state similar to when it was new. This means you’ll need to reconnect to your Wi-Fi networks and re-establish other network connections.
For Wi-Fi, locate your network name (SSID) from the available networks list and select it. Enter the password when prompted. Ensure the password is entered correctly, paying attention to case sensitivity and special characters.
Bluetooth devices will need to be paired again. Initiate pairing mode on both your device and the Bluetooth accessory. Follow the on-screen instructions for successful pairing.
If you are using a VPN, you will need to reconfigure it with the necessary server address, login credentials, and any other required settings.
For mobile devices, ensure mobile data is enabled. This can usually be toggled on or off in the network settings menu. You might need to contact your mobile carrier if data connectivity does not resume after enabling it.
Troubleshooting Issues After Resetting Network Settings

Occasionally, even after a network reset, connectivity problems may persist. This section provides guidance on addressing such scenarios.
Device-Specific Issues
If only one device experiences connection problems, the issue likely lies with that specific device. Restart the device. If the problem remains, consult the device’s troubleshooting documentation or contact its manufacturer’s support.
Incorrect Network Credentials
Double-check your network name (SSID) and password. Ensure you’re connecting to the correct network and using the right password. Case sensitivity matters for passwords.
Hardware Problems
Inspect your network hardware, including your modem and router. Check for loose cables or any visible damage. Try power-cycling your modem and router. If you suspect a hardware fault, contact your internet service provider.
Driver Conflicts (Computers)
On computers, outdated or corrupted network drivers can cause issues. Update your network adapter drivers through your operating system’s device manager.
Preventing Future Network Connectivity Problems
While resetting your network settings can resolve immediate connectivity issues, taking proactive steps can minimize future problems. Regularly updating your network drivers and firmware is crucial. Outdated drivers can lead to compatibility problems and performance degradation, increasing the risk of disconnections.
Monitoring your network activity can also help identify potential issues before they escalate. Unusual bandwidth usage or frequent connection drops might indicate malware or other network problems. Using strong passwords for your router and Wi-Fi network is essential to prevent unauthorized access and maintain network security, further reducing the risk of connectivity disruptions.
Finally, consider documenting your network configuration. Keeping a record of your IP address, DNS server settings, and other important information can streamline the troubleshooting process if future problems arise. This documentation can be invaluable when working with technical support or attempting to diagnose issues independently.
Advanced Network Troubleshooting Tips
If basic troubleshooting and network resets haven’t resolved your connectivity issues, consider these advanced techniques:
Analyzing Network Traffic
Use network monitoring tools to analyze data packets. This can help pinpoint bottlenecks or anomalies affecting performance.
Checking Network Hardware
Inspect physical components like cables, routers, and modems for damage. Faulty hardware can significantly impact connectivity.
Firewall Configuration
Review your firewall settings to ensure they aren’t blocking necessary ports or applications. Incorrectly configured firewalls can prevent connections.
DNS Server Issues
Try using a different DNS server. Sometimes, issues with your internet service provider’s DNS server can cause problems. Consider using a public DNS server like Google Public DNS or Cloudflare DNS.
Understanding the Implications of Resetting Network Settings
Resetting your network settings is a significant step in troubleshooting connectivity problems. It’s crucial to understand the implications before proceeding, as this action reverts various configurations to their default states.
Forgotten Wi-Fi Networks: After a reset, your device will no longer remember saved Wi-Fi networks. You will need to manually reconnect to each network by re-entering the password.
Cleared Bluetooth Pairings: Existing Bluetooth pairings will be erased. You’ll have to pair your Bluetooth devices again.
Reset VPN Settings: Any configured Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) will be removed. You’ll need to re-configure VPN connections with the necessary credentials.
Cellular Settings Reverted: Cellular settings will return to their defaults. This may include APN settings and network selection preferences.